|
||||
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||
Sugar production is a fairly enough complicated process, which includes a great many processing stages. There follows a description in outline of the main stages of sugar production.
A sugar factory's task consists in extracting sugar out of the beet with a chemical transformation. Sugar is already contained in the leaf. The real sugar factory is the beet and essentially its folliage. There takes place photosynsthesis, where along with Co2 of the atmosphere, the soil moisture and the effect of the sunlight are formed the sugars (carbohydrates).
6CO2 + 6H2O -> C6H12O6
The sugars are stored in the root of the beet.
The beet is a bi-ennual plant. Its harvest for industrial use is carried out the first year, the second year it flowers and produces seeds.
The leaves are cut off and the roots are harvested.
The leaves are used for cattle feed or remain in the field for fertilizer, whereas the leaves are transported to the factory for treatment.
The beet contains:
|
|
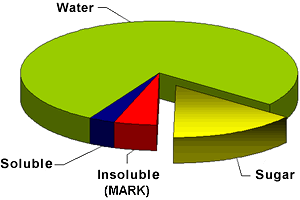 |
The insoluble dry ingredients (cellulose, lignine, pectine, pentozane) form the main components of the by-product called pulp (fresh or dry, pellets). The soluble dry ingredients after removing the 1/3 approx., of the juice in the purification stage, are found again in the molasses, where they bind also a part of sugar.
Out of a treatment of 1.000 tn of beets with a sugar content 14,5% are produced:
Productive data |
Consumptions |
|
Cultivated area of 220.000-225.000 stremmata Production:
(*) Fresh pulp production depends on demand |
Fuel for sugar production: 0,30MWh/tn sugar Fuel for dry pulp driers: 2MWh/tn dry pulp Coke for limekiln: 0,30% on beets Lime-stone: 5,30% on beets
|
Industrial production |